Cyberattacks on businesses are not merely disruptions; they are persistent threats that are escalating in both frequency and sophistication. From ransomware to insider threats, the contemporary digital environment necessitates not only meticulous vigilance but also prompt response.
For enterprise organizations, a single breach can result in substantial financial losses and long-term reputational damage. However, this threat extends beyond multinational corporations; even startups and global enterprises are vulnerable to data breaches, operational disruptions, and eroded customer trust. Without a well-defined and actionable incident response plan (IRP) in place, the consequences of inaction can be catastrophic.
This blog elucidates the paramount importance of incident response planning to establish the fact that it is no longer a matter of convenience but necessity. We will present real-world breaches that underscore the severity of the situation, analyze effective response strategies, and provide practical steps to construct a tailored plan for your organization. In cybersecurity, the inevitability of an attack cannot be overstated; it is a matter of when, not if.
What Is a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan?
A cybersecurity incident response plan outlines how an organization identifies, manages, and recovers from oncoming cyber incidents. It ensures that your organization determines and employs structured, efficient actions before, during, and after a breach to protect critical assets and sustain business continuity.
Key Phases of an Incident Response Plan:
- Threat Detection: Utilize monitoring tools and alerts to detect potential threats or breaches promptly.
- System Containment: Isolate compromised systems to restrict the dissemination of malicious content.
- Malicious Element Removal: Eliminate all malicious elements from affected environments.
- System Restoration: Restore systems, applications, and data in a secure manner to restore normal operations.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the incident to identify root causes, document lessons learned, and enhance future defensive measures.
A clear response plan can drastically cut downtime, speed up recovery, and mitigate both financial and reputational damage. Moreover, it fosters collaboration across IT, legal, and executive teams, transforming chaos into coordinated action. Simply put, a cybersecurity incident response plan is not just technical—it’s an essential business practice.
Why Time Matters During Cyberattacks
In a cyberattack, every minute is of utmost importance. Rapid detection, containment, and response are paramount. IBM’sCost of a Data Breach Report reveals that organizations typically take 280 days to identify and contain breaches, underscoring the prolonged exposure and potential damage.
Prompt action within the initial hours following a breach significantly reduces the attacker’s ability to evade detection, minimize operational disruptions, mitigate financial losses, and minimize reputational damage. Delays at any stage exacerbate manageable incidents into severe crises.
In cybersecurity, preparedness and speed serve as the most effective defenses. A well-trained team with a comprehensive plan distinguishes controlled recoveries from catastrophic outcomes.
Real-Life Lessons in Cyber Preparedness
Let us analyze a few cyber incidents to comprehend the catastrophic consequences they have caused.
Case Study 1: Colonial Pipeline Ransomware (2021)
- Incident: DarkSide ransomware attack disrupted the fuel supply chain.
- Impact: A six-day shutdown led to panic buying and a $4.4 million ransom payment.
- Lesson:
- Enhanced protection of remote access points
- Implementation of multi-factor authentication
- Development of rapid response planning
Case Study 2: MOVEit Transfer Breach (2023)
- Incident: The Clop ransomware exploited a widely-used file transfer software.
- Impact: Affected 2,500 businesses and 94 million users, with damages exceeding $10 billion.
- Lesson: This incident underscores the inherent risks associated with third-party software and emphasizes the paramount importance of robust supply chain security measures.
Case Study 3: Medusa Ransomware Attacks (2021–2025)
- Incident: Targeted phishing attacks and double extortion tactics.
- Impact: Substantial financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational harm.
- Lesson: Reinforces the importance of regular software updates, phishing awareness training, and proactive response plans.
These case studies underscore the evolving nature of cyber threats and the paramount importance of preparedness, regular security assessments, and adaptable response strategies.
Read More: Why Small Businesses Are The New Bullseye For The Threat Actors?
Core Elements of Effective Incident Response Plans
- Detection: Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to provide real-time threat visibility and facilitate proactive threat identification.
- Containment: Implement rapid isolation of affected systems, disable compromised accounts, and segment the network to minimize damage.
- Eradication: Conduct thorough forensic analysis to eliminate all traces of threats, thereby preventing recurrence.
- Recovery: Restore systems and verify data integrity meticulously. Monitor restored environments closely for any suspicious activities.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Review incident timelines and document valuable insights. Enhance future response strategies through continuous improvement.

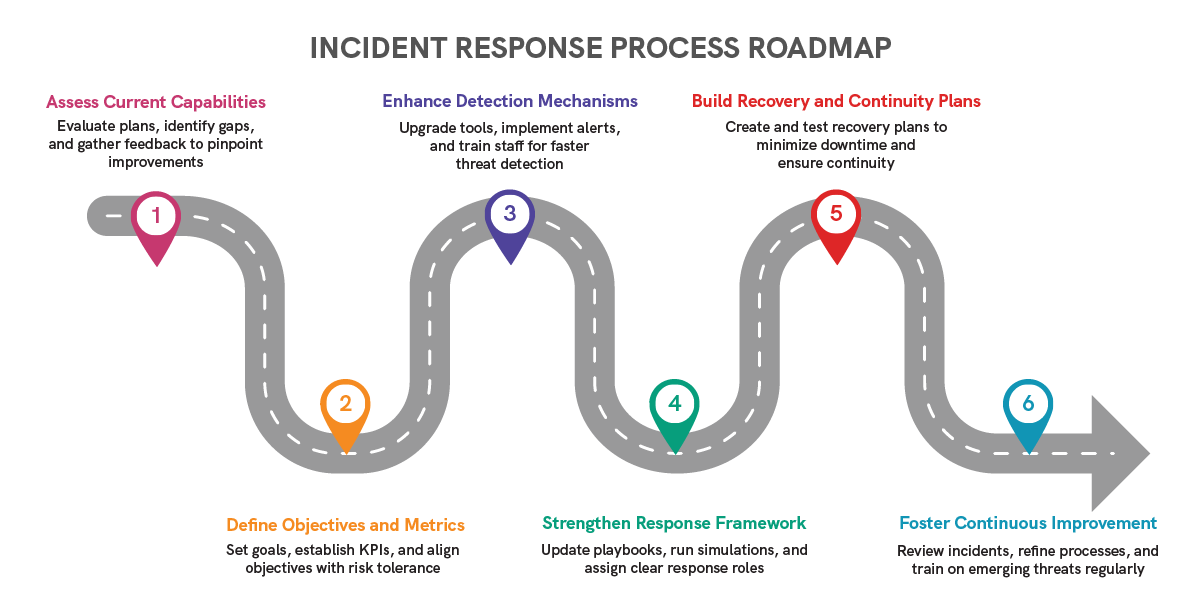
Steps to Create an Incident Response Plan
- Define Your Response Team:
Assemble a cross-functional team comprising experts from IT, legal, communications, and leadership. Clearly define roles and responsibilities and maintain updated contact information.
- Establish Clear Procedures:
Develop actionable, scenario-specific playbooks covering ransomware, phishing, insider threats, and other potential cyberattacks.
- Implement Monitoring Systems:
Deploy Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions for real-time monitoring and incident response.
- Conduct Regular Drills:
Regularly simulate cyberattacks to assess readiness, identify vulnerabilities, and refine response capabilities.
- Stay Updated:
Continuously revise response plans on a quarterly basis or after significant incidents. Incorporate external lessons learned, regulatory updates, and emerging threats.
Read More: Understanding Shadow AI: Why Organizations Cannot Afford to Overlook This Hidden Threat
Importance of Continuous Improvement
Cyber threats persistently evolve, necessitating continuous improvement vital. Post-incident evaluations pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, thereby fortifying defense strategies and protocols. Quarterly updates ensure that response remains proactive and effective, effectively addressing emerging vulnerabilities and threats.
Ongoing refinement transforms static response plans into dynamic, strategic defenses that align with the evolving threat landscape.
Costs of Ignoring Incident Response Planning
Operating without a well-defined incident response plan can lead to substantial financial losses. The global average cost of a breach exceeds $4 million, excluding regulatory penalties, legal actions, and reputational damage. Publicly traded companies are particularly susceptible to such risks, as they may experience declining stock value and diminished investor confidence.
By investing in robust incident response planning, organizations can significantly mitigate financial exposure, operational disruptions, and long-term damage.
Conclusion
Cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent. However, preparedness is the key to mitigating their impact. A structured incident response plan enables swift and controlled actions, minimizing harm, reducing costs, and preserving organizational integrity.
Do not wait for a breach to reveal vulnerabilities. Proactively develop, practice, and refine your incident response plan. Your organization’s resilience depends on your preparedness today.