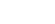Despite being pricey, macOS-driven computers, popularly known as Macs, offer many advantages, especially regarding their security and usability. Apple consistently works to safeguard its users by employing various state-of-the-art security measures. However, like other available operating systems, macOS is only partially immune to new-age cyber threats despite its extensive safeguards.
Over the years, our K7 Telemetry has seen an upward trend in macOS malware going “wild” or being actively exploited in bilateral attacks.
Types of macOS Malware Found in the Wild
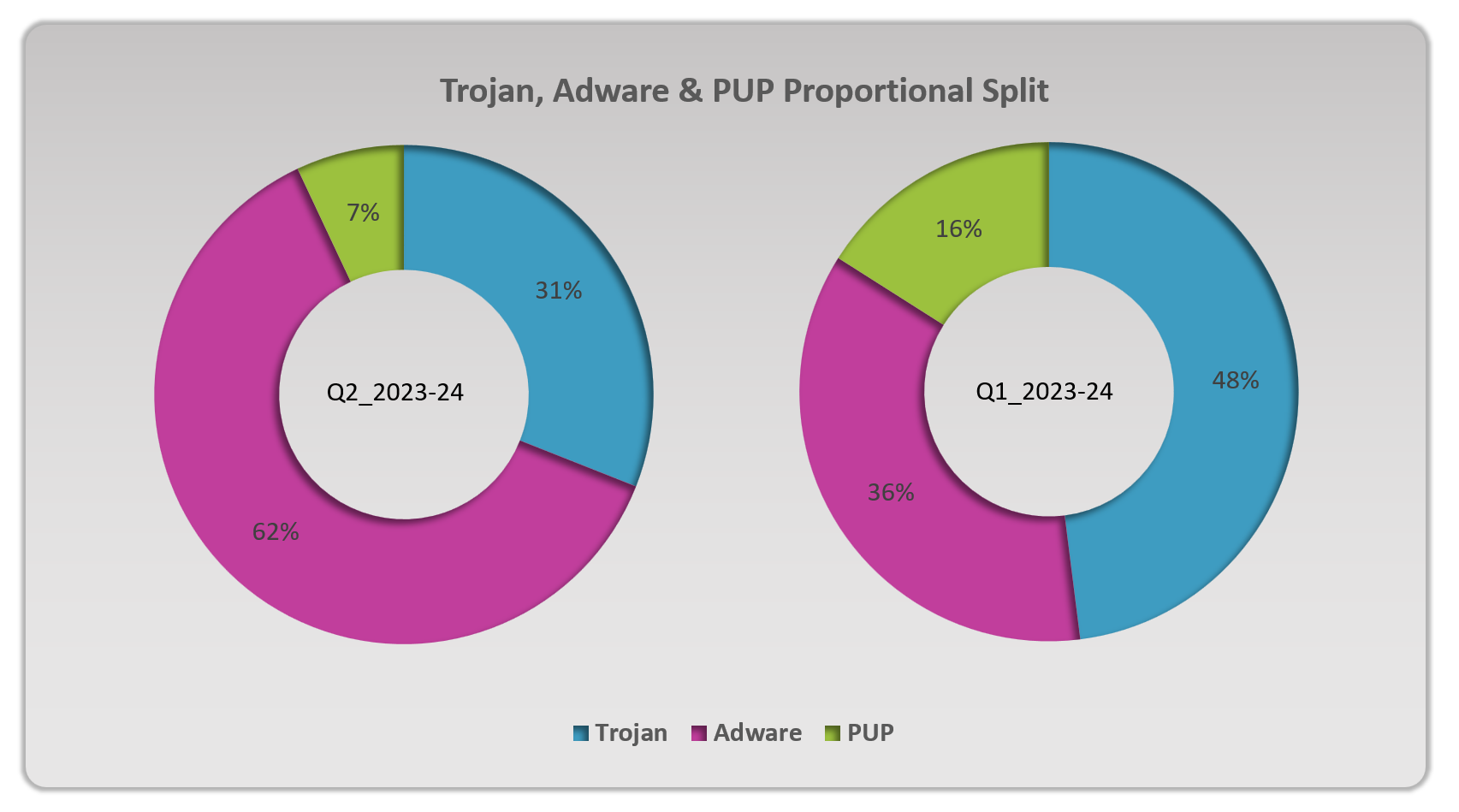
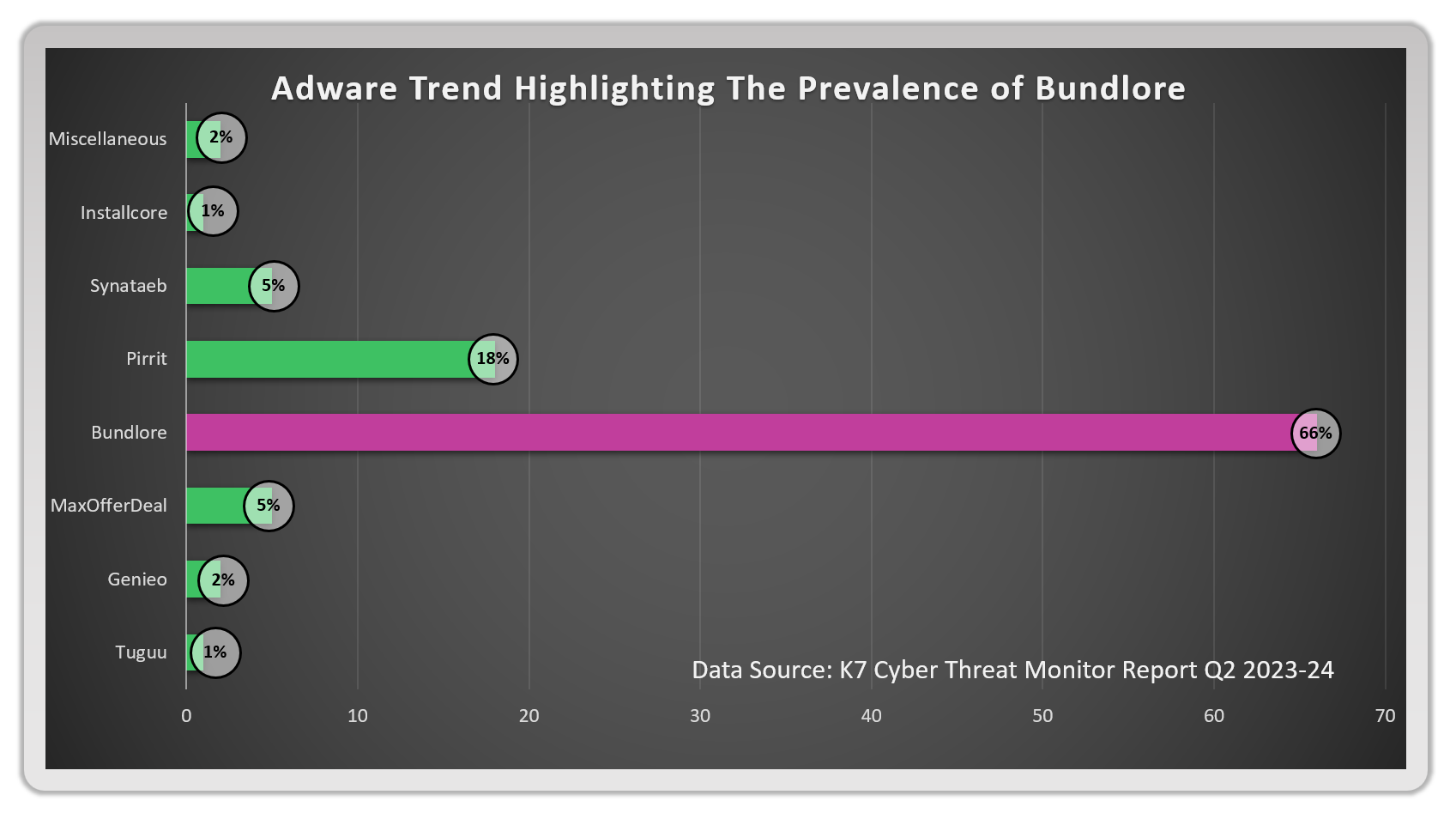
Various types of macOS malware have been observed in the wild, from adware to ransomware—the TrojanDownloader.Adload, for instance, accounted for around 66% of all detections, making it the most common threat. Closely following this Trojan are various adware such as Bnodlero and Bundlore that have plagued macOS systems.
macOS Malware Distribution in 2023-24
Over the years, malware distribution within macOS systems has grown increasingly complex. There are several widespread methods used to unfurl several families of malware, including the utilization of phishing emails, different types of social engineering tactics, insecure downloads, harmful ads, false flash updates, and more.
Go-based payloads, like Geacon, are also on the rise. Geacon is a payload used to simulate enterprise-level apps to steal confidential data. Due to their widespread use, these phony enterprise-level apps allow attackers enormous variety and dynamism while increasing potential damage. Other prevalent campaigns throughout the year are as follows:
Unpacking Adload, a prominent macOS malware
Adload, one of the most widespread malware families, shows how built-in utilities in macOS like chmod, xattr, and ioreg are abused. It redirects user traffic through the attacker’s servers using a Man-in-the-Middle attack. Installing a web proxy lets the attacker steal search engine results and inject advertising into victim-visited websites.
In addition to dropping other payloads, Adload creates Plist files in LaunchAgents or LaunchDaemons to stay on the infected device. It often installs LaunchAgents, LaunchDaemons, and bi-hourly cronjobs for persistence.
Read the detailed K7 Quarterly Cyber Threat Monitor report, showcasing a granular view of the contemporary threat landscape.
Downfall Vulnerability: Intel-Processor Macs at Risk
Intel-based Macs from 2015 or later and late 2015 iMacs were vulnerable to the Downfall vulnerability in August 2023. Apple’s macOS update to rewrite CPU microcode is intended to fix this.
Exploit HVNC: Remote Control of Macs
In the same month, Exploit HVNC was identified, using Hidden Virtual Network Computing (HVNC) to infiltrate a Mac device remotely without the user’s knowledge. It was reported by the security firm, Guards.
ShadowVault Malware: User Data Breach
In July 2023, a new malware named ShadowVault was discovered, which can steal usernames, passwords, credit card information, and data from cryptocurrency wallets.
JokerSpy: System Control via Backdoor
The JokerSpy malware surfaced in June 2023, enabling attackers to control systems, run further exploits, and monitor users’ behaviour. This malware can steal login credentials and cryptocurrency wallets.
AMOS – Theft of Important Information
In April 2023, the Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS) appeared. This malware targets macOS devices and steals essential information, including keychain and user account passwords. AMOS generally spreads through unsigned disk image files (.dmg).
RustBucket: A Hidden Threat
In April 2023, RustBucket also appeared. Viewing a PDF file activates this AppleScript file as a PDF Viewer. Victims were advised to download a ‘unique’ program for secure document viewing, ‘Internal PDF Viewer.’ These users evaded Apple’s security because they believed this program was necessary for transaction secrecy. While downloading and running malware from the attacker’s C2, the infected PDF viewer displayed the victim the intended document.
MacStealer: Undermining Browser Safety
In March 2023, the MacStealer malware was found. MacStealer can discover passwords, cookies and credit card details from Firefox, Google Chrome, and Brave browsers, even extracting the KeyChain database.
XMRig: Lurking in Pirated Software
In February 2023, the crypto-mining software, XMRig, was detected. This mining software was found in pirated copies of Final Cut Pro downloaded from unauthorized distribution points online. It can avoid detection by the Activity Monitor app by stopping when the Activity Monitor runs and resuming when the user quits the app.
The Mythic & Poseidon Story
Attackers employ Mythic, an open-source command and control framework, to launch macOS malware like Poseidon. Poseidon’s implant executes command sequences to infiltrate macOS systems.
Bad actors took over Cobalt Strike’s C2 management suite for similar goals but with different dynamics. Its framework is sturdy but less flexible than Mythic and Poseidon.
In “living off the orchard” alias LOLBin attacks, attackers employ system_profiler, sw_vers, and curl to bypass security constraints.
Measures to Prevent Security Threats in macOS
Given its security measures, MacOS is quieter and more cyber-resistant than other Operating Systems. With today’s sophisticated cyber-attacks, no system is incorruptible. It’s essential to know how to protect macOS from such risks.
Apple has added many security features to protect the OS, starting with macOS Mojave.
Regular Updates
Keep your system updated. Each Apple update addresses issues and improves security. Check machine Preferences -> Software Update to see if your machine has the latest updates and fixes.
Disable Automatic Login
Avoiding automatic log-in can thwart any unwanted access to your macOS system. This feature can be managed under System Preferences -> Users & Groups -> Login Options -> Automatic login.
Enable Firewall
The built-in firewall forms a defense line against unauthorized access or hacking attempts. Go to System Preferences -> Security & Privacy -> Firewall to enable it. If the firewall is turned off, click on the padlock to make changes.
Install Reliable Security Software
Although macOS has robust built-in security, installing additional reliable third-party security software like award-winning K7 Antivirus for macOS provides ransomware protection and safeguards the system by blocking, identifying, and eradicating cyber threats in real-time without impacting the system performance. Additionally, it implements a sophisticated Smart Firewall and an Intrusion Detection feature to fortify defenses against any hacker infiltration. It also offers web and webcam protection, identifying and vaccinating rogue USB devices in real-time, Wi-Fi advisor to spot malicious hotspots and many more.
Avoid Downloading Things from Unauthenticated Websites
Malware usually finds its way into systems via unsecured websites. Stick to trusted websites and the Mac App Store for all your downloads.
Take Advantage of The Inbuilt FileVault
FileVault is a disk encryption program available in Mac OS X 10.3 and, later, implementing XTS-AES-128 encryption with a 256-bit key to eliminate unauthorized access to information on the startup disk. To turn this on, navigate to System Preferences -> Security & Privacy -> FileVault.
Lockdown mode in macOS Sonoma
Lockdown Mode is an innovative feature in macOS Sonoma designed to secure sensitive information on your Mac tightly. Ideally, this mode is for use in dire circumstances when there’s a suspected risk of cyberattacks. This feature can offer an augmented degree of security for individuals in sectors handling sensitive data or those with highly classified details stored on their Mac. The same is also available for other Apple devices such as iPhone, iPad and Apple Watches.