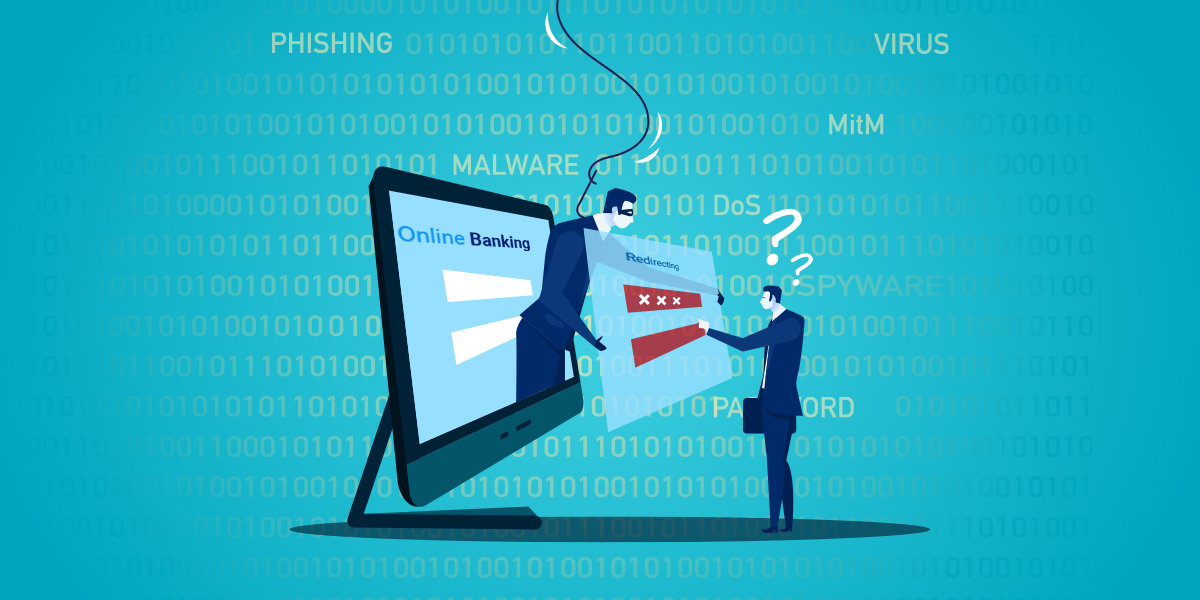
In this blog, we would discuss the most unpredictable and infamous phishing technique called Pharming to carry forward with our Social Engineering Knowhow series. Pharming is a portmanteau of the words phishing and farming, and get identified as one of the most notorious social engineering attacks. Unlike other social engineering techniques such as Phishing, SMiShing, or Vishing, Pharming doesn’t require any human interaction to hoodwink its victims.
In a nutshell, Pharming, popularly known as drive-by Pharming, gets widely used against the home, SOHO, and SME users primarily via two methods- DNS server poisoning and malware driven Pharming.
DNS Server Poisoning
To understand how a pharming attack gets executed via poisoning a DNS server, you should know all about a DNS server.
DNS or Domain Name System servers are computers, services, or other resources connected to a private network. These servers are primarily responsible for directing your internet traffic to a legitimate server IP addresses of any website you have requested.
DNS functions quite alike the contact app of your smartphone. The contact app saves a person’s number combined with their name, so whenever we need to call someone, we search for the respective persons’ name and tap on it. Once you tap on the title, the contact app would place a call to the connected number associated with it.
Similarly, when you enter a website URL (such as www.k7computing.com) in the address bar of a web browser, the DNS system comes into play. It converts the URL into a corresponding IP address (for instance, 126.81.206.69).
A DNS system keeps all the pre-visited URLs combined with the corresponding IP addresses and gets known as a DNS cache.
And through a DNS cache poisoning method, an attacker can swap all the legitimate IP addresses that exist on the DNS Server with malicious website IPs.
Read More- Social Engineering And The Psychology Of Falling Prey To Cybercriminals
DNS Server Poisoning- How it Works
Modern pharming attacks are also capable of exploiting common security vulnerabilities found in a home, SOHO, and SME routers to gain access to the admin console. Once compromised, the con artists modify the DNS setting of the compromised router redirecting to their DNS server. The Pharming process involves forging the DNS cache and changing the DNS server settings to ensure that whenever a victim navigates to any website. The corrupt DNS cache would redirect the traffic to a fraudulent site to do the damage.
Money-motivated cybercriminals often use DNS poisoning pharming attacks to execute Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and steal personal, business, and banking information. DNS poisoning system also gets prevalently used to implement man-in-the-middle attacks and to install malware into the system.
Malware driven Pharming
Unlike the DNS Server poisoning method, malware powered pharming attack lures the victim primarily via email-phishing.
The cybercriminal often tricks the victims via a legit-looking email loaded with a malicious link or attachment. Once the victim clicks on the link or downloads the attachment, the payload reroutes the victims’ internet traffic to a malicious impersonated website. It also obtains complete control over the victim’s internet traffic.
In malware driven pharming attacks, the malicious payload rewrites the local host files of the victims’ machine to ensure the internet traffic gets driven to fraudulent sites regardless of the website URL they type on the browsers address bar.
Read More- Social Engineering Knowhow 2: Everything You Should Know About Phishing
Detecting a Pharming Attack
Due to the complex structure of its kill chain, pharming attacks are tough to detect and get by. Sophisticated pharming attacks often succeed to mislead the system installed firewall and continue its operation. Modern pharming attacks are also tough to identify for their clandestine nature. To stay safe from any such sophisticated cyberattacks, SOHOs, SMEs, and Enterprises should educate its employees about basic cyber hygiene principles.
The cybersecurity education and awareness program should elaborate on modern attack trends, detection measures to identify a fishy site, and things to do if they encounter anything malicious.
Read More- Social Engineering Knowhow 3: All You Need To Know About Vishing And SMiShing
Go-to Guide for the Admins
Administrators should also keep track of each connected device to the network and the vulnerabilities they introduce. Many commercial routers and embedded systems exist with commonly known unpatched vulnerabilities, thus often sets the red carpet for the con artists.
Running systems on dated and unpatched operating systems or application software could also lead your network to breaches.
You should always pay close attention to emails and never click or share any suspicious email with attachments.
Watch out for the websites you or your users’ visit. Malicious websites often intend to deliver malware payloads or browser extensions triggered to modify your DNS cache.
Patch all the routers installed on your network. If any router manufacturer has stopped offering updates, you should either swap the router with the latest one or download a third-party firmware available for the router.
You should also ensure that each URL you visit doesn’t have any typographical errors. Make sure the site has an HTTPS at the beginning of the URL.
Notice the website logo, content structure, font size, and color layout to find out if anything is fishy.
Flash your DNS cache by navigating to Start>>run or press key sequence Windows+R. Once the run dialogue box appears, type CMD and hit enter. Type ifconfig /flushdns and press enter button. You can also flash your system DNS cache via Windows PowerShell through the command Clear-DnsClientCache.
Finally, ensure all your systems have a trusted endpoint security software like K7 Endpoint Security.