In recent times, a barrage of AI tools, including DeepSeek, have garnered overnight popularity among enterprise employees seeking to streamline various tasks at ease. Even though these applications offer quick solutions, making them appealing for daily work challenges, the allure of these tools often overshadows potential pitfalls and the approaching murkiness of the digital world. Unauthorized AI applications can expose sensitive business data, leading to numerous types of security breaches including data and patent leaks. Additionally, they may not necessarily comply with industry regulations, posing compliance risks. Ethical concerns such as biased or discriminatory outputs may also arise, as unvetted AI tools often produce biased outputs, and thus damage enterprises’ reputations.
To illustrate the prevalence of this issue, consider that nearly 83% of all legal documents shared with AI tools reportedly go through non-corporate accounts. Furthermore, about half of all source code is shared similarly.
This blog will show you the risks of Shadow AI and how to stop them before they spiral out of control.
What Is Shadow AI?
Shadow AI happens when employees use AI tools without approval from the accountable authorities. These tools often include chatbots, data analysis platforms, automation software, etc. Employees adopt them to solve problems without hassles, bypassing IT and compliance teams. However, this unregulated use can often lead to data leaks, ethical violations, and operational inefficiencies.
For example, an employee might use a free AI transcription tool for confidential meetings, exposing sensitive data to third-party servers. Such actions can have severe consequences for organizations.
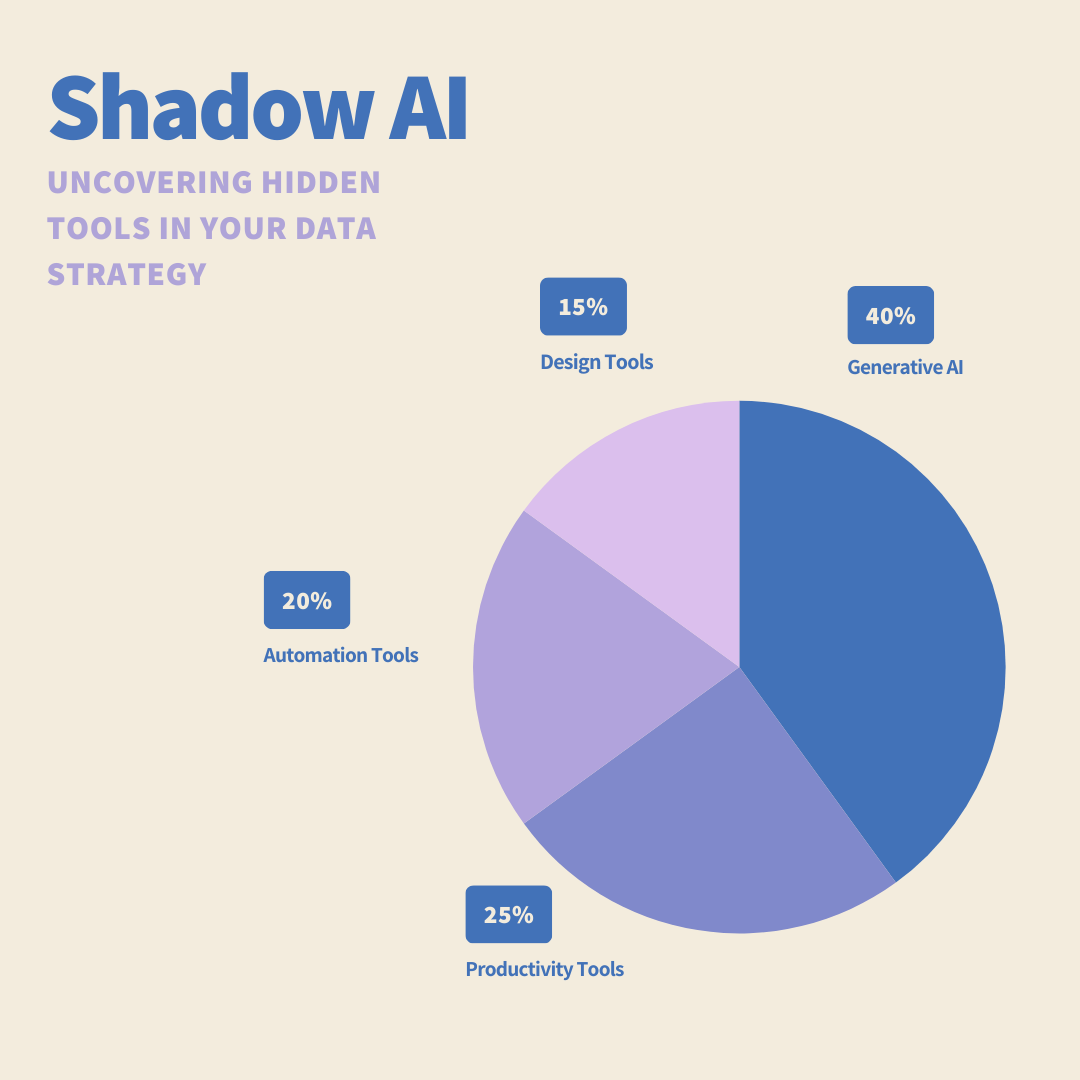
The list of Shadow AI tools can range between:
- Generative AI Tools: The list includes AI-driven chatbots, text generators, and image-creation tools that employees use without official approval. Examples include ChatGPT, Jasper, MidJourney, and DALL·E, which can generate text, images, or code but may inadvertently process sensitive company data if used carelessly.
- Automation Bots: These are AI-powered tools that automate repetitive tasks but may operate outside of IT’s control, posing security and compliance risks. Examples include Zapier, UiPath, and Microsoft Power Automate, which can integrate different applications and move data across systems, potentially exposing confidential information.
- Machine Learning Models: Employees may develop or use machine learning models without implementing necessary security and privacy controls. These models can analyze large datasets but might not be vetted for compliance. Examples include Google AutoML, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, which allow users to build custom AI models but could expose proprietary data if misconfigured.
- AI Integrations: Many applications now offer AI-powered plugins and add-ons that users can install without security approval. These tools can introduce vulnerabilities if they have weak access controls or share data with third parties. Examples include AI-powered CRM integrations like Salesforce Einstein, writing assistance tools, and Notion AI for document automation.
Why Shadow AI Happens
The most interesting fact about Shadow AI is it doesn’t always arrive through bad intentions. It often starts with employees trying to solve problems quickly. Enterprise employees often embrace them because of:
- Need for Speed: AI tools help employees work faster, which often urges them to skip formal approvals.
- Lack of Awareness: Many don’t realize AI tools can pose massive security risks.
- Slow Approval Processes: Long IT reviews push employees to come up with their own solutions.
- Easy Access: Most AI tools are available just a click away and don’t require any technical expertise to work on.
Read More: Shadow IT, the most significant cybersecurity risk explained
The Hidden Dangers of Shadow AI
Let’s understand how shadow AI tools can pose significant risks while working with enterprise data including codes in a much-elaborated manner.
Security Risks: A Backdoor for Cyber Threats
Shadow AI creates a range of security gaps that traditional defenses often fail to detect. These risks can lead to severe cybersecurity incidents, without proper oversight, including data breaches, compliance violations, and system compromises. Some of the most critical risks include:
- Data Exposure: Employees may input sensitive company data, customer information, or proprietary details into unsecured AI platforms. If these tools lack proper data protection mechanisms, they can become a goldmine for cybercriminals, leading to data leaks, insider threats, or regulatory non-compliance.
- Weak Security Controls: Many AI tools, especially those developed without security in mind, often lack essential safeguards such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access control policies. This makes them easy targets for attackers who can intercept, manipulate, or extract sensitive data.
- Model Exploitation: Cybercriminals can manipulate AI models using adversarial attacks—subtly altering input data to deceive or corrupt AI decision-making. This can lead to false predictions, biased outputs, or security bypasses that can be exploited for fraud, misinformation, or unauthorized access.
- Unsecured APIs: Many Shadow AI tools rely on APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to integrate with other systems. However, if these APIs are not properly secured, they can become entry points for cyberattacks, enabling hackers to extract data, inject malicious code, or disrupt services through API abuse.
Read More: Navigating the Deepfake Phishing: Understanding and Combating AI-Enabled Phishing
Compliance Risks: Violating Laws Without Knowing It
However, using Shadow AI can inadvertently put organizations at risk of regulatory violations, often without their awareness. Many industries are bound by strict compliance frameworks that dictate how data should be collected, stored, and processed. When AI tools operate outside of official security and compliance protocols, they can introduce serious legal and financial risks. Key compliance challenges include:
- Data Protection Issues: Many AI tools process personal or sensitive data without built-in compliance safeguards. If an employee unknowingly inputs personally identifiable information (PII), healthcare records, or financial data into an unapproved AI system, it can violate major privacy regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines, reputational damage, and legal action.
- No Audit Trails: Compliance frameworks require organizations to maintain detailed records of data access, modifications, and usage. Shadow AI tools often lack proper logging and tracking mechanisms, making it impossible to conduct audits or demonstrate regulatory compliance. Without visibility into how AI systems process and store data, organizations risk failing compliance assessments and facing penalties.
- Cross-Border Risks: Many AI tools operate on cloud-based platforms that store and process data in multiple jurisdictions. This can lead to violations of data sovereignty laws and restrictions on international data transfers. For example, under India’s Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, personal data can only be transferred to countries that India designates as “trusted”. If a company unknowingly uses an AI service hosted in a non-compliant country, it could face legal consequences for unauthorized data transfers. A similar thing can happen with GDPR and other countries’ acts.
Ethical Risks: Bias and Bad Decisions
Unvetted AI tools can create severe ethical problems, leading to numerous discrepancies impacting fairness, accountability, and transparency. Key concerns include:
- Built-in Bias: AI models learn from historical data, which can contain biases related to gender, race, or socioeconomic status. These biases can lead to discriminatory hiring decisions, unfair loan approvals, or biased legal judgments.
- Lack of Transparency: Many AI systems function as “black boxes,” making decisions without clear explanations. This lack of accountability can be problematic in high-stakes scenarios like healthcare diagnoses, credit scoring, or legal rulings, where individuals deserve to know how outcomes are determined.
- Reputation Damage: When AI is deployed irresponsibly, it can erode customer trust and damage a company’s brand. High-profile cases of AI failures—such as biased facial recognition systems or chatbots generating offensive content—can spark public backlash, lawsuits, and regulatory penalties.
Business Disruptions: Productivity at a Cost
While Shadow AI promises efficiency, it often creates more problems than solutions, leading to operational inefficiencies, system conflicts, and unreliable decision-making. Without IT oversight, these tools can disrupt workflows instead of enhancing them, resulting in hidden costs and risks. Key challenges include:
- Over-Reliance: Teams may become dependent on AI tools that lack enterprise support, security updates, or long-term viability leading to lost productivity, missed deadlines, and increased operational risks.
- Inconsistent Results: AI tools require proper tuning, training, and quality control. Without these, they can produce unreliable, inaccurate, or misleading outputs, leading to poor business decisions, flawed reports, and reputational damage.
- Integration Issues: Shadow AI often lacks seamless compatibility with existing enterprise software, databases, and workflows. Unapproved tools may cause system conflicts, data silos, or unexpected downtime, disrupting operations.
Read More: The Growing Infamy of Deepfake Technology and How to Combat It
How to Identify and Manage Shadow AI Risks
Shadow AI is thriving quietly in workplaces, bringing hidden security, compliance, and ethical risks. While it makes the job easy for many employees daily job, it can lead to data breaches, legal troubles, and reputational harm, if left unchecked.
Building a Secure and Responsible AI Framework
As organizations increasingly adopt AI, Shadow AI—unapproved and unmanaged AI tools—can introduce security, compliance, and operational risks. To mitigate these risks, businesses must establish strong AI governance, enhance visibility, promote responsible usage, and secure data at every level. Here’s how:
- Set Clear AI Governance Policies: AI adoption can become chaotic, without well-defined policies, leading to security gaps and regulatory violations.
- Define Acceptable Use: Develop a comprehensive list of approved AI tools, specifying permitted use cases, access levels, and data-sharing restrictions. Clearly outline which tools are prohibited and why.
- Assign Oversight: Form an AI governance team consisting of IT, security, legal, and compliance experts. This team should review AI adoption, assess risks, and ensure adherence to regulations.
- Policy Awareness: Employees must understand AI-related risks and responsibilities. Conduct regular training sessions, awareness programs, and hands-on workshops to reinforce secure and compliant AI usage.
Improve Visibility Across the Organization
Shadow AI often operates under the radar, bypassing security controls. Organizations must enhance visibility to detect and manage unauthorized AI tools before they pose a threat.
- Use Discovery Tools: Deploy AI monitoring solutions that scan networks for unapproved AI applications and integrations, flagging potential security risks.
- Monitor Data Traffic: Analyze API calls and data flows to identify unusual patterns indicating unauthorized AI tool usage or potential data exfiltration.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule periodic reviews of AI tools in use, evaluating their access permissions, compliance status, and security posture.
Foster a Culture of AI Responsibility
AI governance is not just about rules—it requires a company-wide shift toward responsible AI adoption. Encouraging ethical and secure AI practices reduces the likelihood of Shadow AI threats.
- Educate Employees: Train teams on the risks of Shadow AI, secure data handling, and the potential legal and reputational impact of unauthorized AI usage.
- Encourage Transparency: Establish a simple, well-defined process for employees to request new AI tools instead of seeking unapproved alternatives.
- Reward Compliance: Recognize and incentivize teams that follow governance policies, fostering a security-first mindset across the organization.
Secure Data at Every Level
AI tools often process sensitive corporate, customer, and financial data. A robust security framework ensures that data remains protected, even when AI is implemented.
- Classify and Protect Data: Implement data classification policies to distinguish between public, internal, confidential, and highly sensitive data. Encrypt sensitive information both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Zero Trust Security: Enforce a Zero Trust model, granting AI tools the least privilege necessary based on user roles and data sensitivity. Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict access controls for AI-related activities.
- Vendor Risk Management: Third-party AI providers can introduce security risks. Thoroughly vet AI vendors for compliance with industry standards, conduct security assessments and establish clear data protection agreements before deployment.