Cybersecurity, Information Security, and Network Security are terms that are frequently encountered when discussing enterprise digital security. Questions arise on the differences between the three and which of the three an organisation needs, or the context in which each is required. We will discuss each of these and their role in enterprise digital security.
Are Cybersecurity, Information Security, and Network Security Related Terms?
Cybersecurity, Information Security, and Network Security are related terms. There is significant overlap between the terms but the distinctions do matter. Cybersecurity is an overarching term that includes both information security and network security. Cybersecurity, however, is limited to an organisation’s digital assets. Information security’s ambit includes physical forms of data in addition to digital and therefore extends beyond cybersecurity.
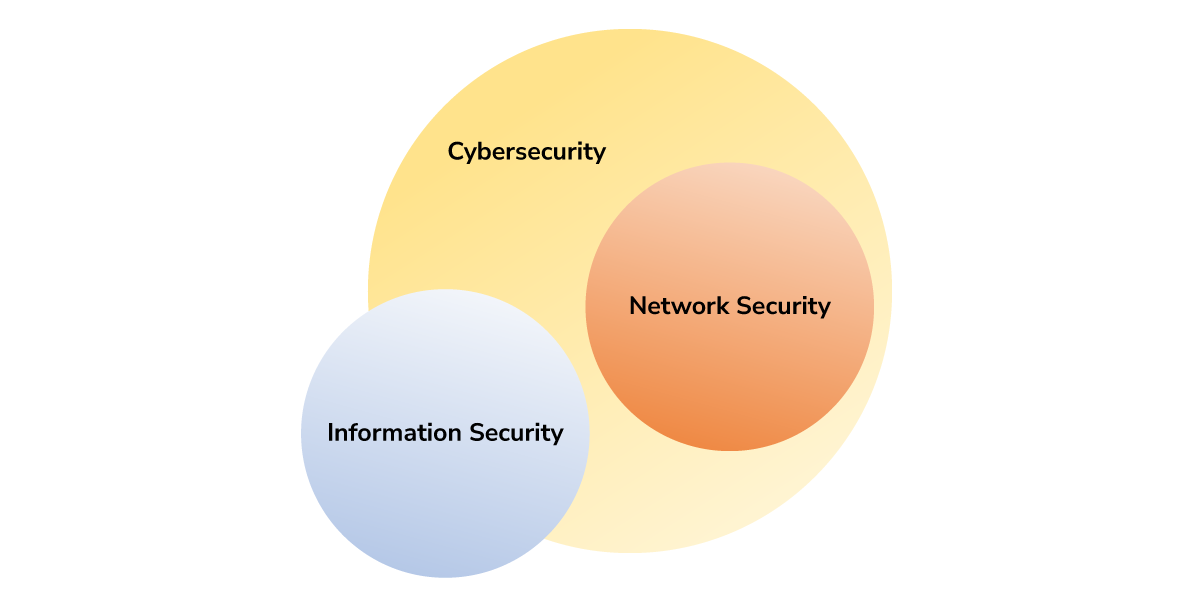
Cybersecurity, Information Security & Network Security
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity refers to any, and all, measures to secure an organisation’s digital assets. Cybersecurity will therefore include
- Device Security
- Endpoint Security (EPS) – Individual device protection against malware, phishing, ransomware, zero-day attacks, and many other cyberthreats, with centralised control
- Enhanced Detection and Response (EDR) – Includes manual or automated responses to cybersecurity events
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR) – Integrates all devices and traces suspicious activity across devices and digital entities to identify emerging cyberattacks and alert security teams before the attack can launch
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) – Cybersecurity for mobile devices that includes mobile-specific defences such as tracking missing devices and wiping lost/stolen devices that cannot be retrieved
- Authentication – Zero Trust and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- IoT Security – Security for any non-computing device connected to the network, such as networked printers, HVAC sensors, and smart locks
- User/Identity Security
- Password Manager – Securely stores and fills passwords to prevent credential theft
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Additional credential security to prevent compromise even if passwords are stolen, such as two-factor authentication that requires both a password and OTP
- Identity Access Management (IAM) – Ensures that genuine users have permitted access to enterprise resources
- User and Entity Behaviour Analytics (UEBA) – Profiles and establishes a behaviour baseline, and identifies deviations from the baseline to flag suspicious activity
- Zero Trust – A strategy/architecture that focuses on always verifying if the user/device has the requisite access privileges before granting access to any resource, and never assuming that the user/device has been verified merely because they are present in the network
- Compliance – In addition to defending against cyberattacks, cybersecurity also involves complying with cybersecurity and data privacy regulations such as ADHICS, GDPR, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS
- Policies – Documented cybersecurity policies that establish the standards, parameters, and protocols to be followed to maintain enterprise cybersecurity, including cybersecurity for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) and remote/hybrid working, with penalties for non-compliance
- Services
- VAPT – Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing to test the enterprise’s digital defences against simulated attacks
- GRC – Governance, Risk, and Compliance practices that emphasise financial and operational risk management to align cybersecurity with strategic objectives and avoid operational inefficiency
- Red Team Assessment – Offensive cybersecurity evaluation that utilises the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) used in real-world cyberattacks to test the business’s ability to detect, respond to, and contain threats
- Information Security Assurance – Real-time improvement of enterprise cybersecurity posture covering legal, physical, and technical controls
- Integrated Managed Services – Integration of cybersecurity and compliance with continuous monitoring of the organisation’s digital ecosystem to achieve a perpetually elevated cybersecurity posture
- Platforms
- SIEM – Security Information and Event Management gathers, analyses, and correlates security event data from across the enterprise to identify attacks
- SOC – Security Operations Centre that is manned by security analysts to continuously monitor enterprise digital activity and respond to security incidents
- SOAR – Security Orchestration, Automation and Response uses automation and workflows to improve Mean-Time-To-Response (MTTR)
Information Security
As mentioned above, Information Security is both a part of cybersecurity (relating to digital data) and broader than cybersecurity (relating to physical data). Information security is critical to maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
Digital Information Security
Digital Information Security pertains to the protection of data stored and transmitted in digital form. Protection includes protection from unauthorised access, theft, modification, and deletion. Many of the elements discussed under cybersecurity will also apply to information security as they protect data, such as GRC, IAM, MFA, Policies, and Zero Trust. Specific features within solutions also contribute to data protection e.g., K7 Endpoint Security supports blocking of external devices, which prevents data from being copied to or from USB storage media. Other elements of digital information security include
- File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) – Monitors the creation, deletion, movement, or modification of files stored in critical areas relating to patents, intellectual property, and other crown jewels of enterprise data
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) – Monitors sensitive data at rest and in motion to detect unauthorised access, use, or transfer. DLP is not restricted to technology, and integrates people and processes in the data protection strategy
- G Suite Segmentation – Businesses that use G Suite/Google Workspace are exposed to the risk of theft of sensitive data as employees may be able to access their personal Gmail accounts or G Suite accounts linked to another domain to transfer business data. G Suite Segmentation, available in K7 Endpoint Security, helps maintain information security by allowing access to the official G Suite account and blocking access to personal Gmail accounts and G Suite accounts linked to other domains
- Data Backup – A data backup strategy that follows the 3-2-1 rule (3 copies, 2 types of media, 1 off-site copy) protects against data loss from destructive cyberattacks, such as ransomware, and disk failure
Physical Information Security
Business data that is stored in physical form, such as printouts, may be stolen or modified. Business data that is stored in digital form may also be stolen or modified through physical access. Physical information security, therefore, will include
- Print Security – Print privileges must be restricted and list of files printed must be maintained to verify that sensitive documents are not printed without authorisation. Critical documents must be watermarked to enable identifying the source if a leak occurs. Employees must not be allowed to carry printed copies into or outside the facility. Hard copies, including paper in trash cans, should be shredded before disposal
- Device Security – Devices should not be allowed to be carried outside the facility without authorisation. Laptops that can be expected to be carried outside the facility should have disk encryption and remote wipe enabled. Devices should be wiped before disposal
- Access Restrictions – Physical access to the facility should be restricted to prevent entry of unauthorised users. User access within the facility should also be restricted for critical areas such as server rooms and data banks to prevent intentional or accidental compromise
Network Security
The IT network of the organisation is the backbone of digital infrastructure and must be secured. Network security is a subset of cybersecurity and involves
- Perimeter Security – All data flowing into and out of the facility must pass through a network firewall. This ensures that suspicious data traffic is stopped at the network perimeter. The network firewall is distinct from the host-based firewalls that are included with endpoint security solutions that monitor data flowing into and out of an individual device
- Network Segmentation – The network should be segmented into sub networks to isolate attacks within a sub network and prevent them from spreading across the organisation. Network segmentation can be achieved using K7 Next Generation Firewall
- VPN – A Virtual Private Network allows remote employees and branch offices to connect to the head office and access IT resources through a secure, encrypted connection. Enterprise VPN can be enabled through the K7 VPN Concentrator
- SD-WAN – A Software-Defined Wide Area Network provides both stable and secure connectivity for enterprises with distributed operations that utilise on-premises data centres, public or private clouds, and SaaS services
- User Management – Network user management, including authenticating of users, is important for both wired and wireless networks, and particularly for wireless networks as a physical interface is not required to access the enterprise network
Enterprise cybersecurity encompasses many components that must work in tandem to protect business operations. Every business, however, does not need every component, and must choose the cybersecurity, information security, and network security components that are best suited for their operations and growth strategies. K7 Security’s wide portfolio of enterprise cybersecurity solutions can help you gain cybersecurity appropriate to your risk exposure and compliance requirements.
FAQs
1. Which do I need? Cybersecurity, Information Security, or Network Security?
Cybersecurity includes information security and network security, and therefore you primarily need cybersecurity, taking care to choose the components of cybersecurity that are appropriate for your business. Information security includes physical security which falls outside the scope of cybersecurity; ensure you are including physical security in your data protection strategy.
2. Are cybersecurity products sufficient to protect any scale of operations?
Smaller organisations may be able to gain sufficient protection purely through cybersecurity products but larger organisations will require additional cybersecurity services to secure their operations. Compliance obligations, irrespective of scale of operations, may make some cybersecurity services mandatory for businesses e.g., SEBI mandates Regulated Entities to conduct VAPT exercises at regular intervals.
3. How do I maintain cybersecurity when employees are working from home?
If employees are using personal devices to work from home, they must have robust antivirus like K7 Ultimate Security installed on their devices and keep the antivirus updated. If they are using a business device, a cloud-based endpoint security solution like K7 Cloud Endpoint Security must be used to protect their device and ensure it syncs with the console even when they are outside the business network. In both cases, the employees must adhere to the enterprise cybersecurity policy and use a business VPN to communicate securely with the enterprise.