Ransomware has always been in the headlines for its disruptive nature and these days there has been a spurt in these attacks with the rise in the “triple extortion” technique, whereby threat actors, not only steal sensitive data from the organisation, and threaten them that their data would be released in the darknet, but also target their customers and business partners. Also, even if the ransom is paid, there is still a risk for organisations as their data can be put for sale in the darknet.
This blog is also for awareness about phishing and a continuation of the previous blog. This is about how phishing can be used as an attack vector or should it be called the predecessor to spread dangerous malware and ransomware.
Phishing has become the most used attack vector to spread ransomware these days. Threat actors use links or attachments to befool users into doing the expected action. These phishing emails usually come from known contacts or the employee’s superiors, thereby forcing users inadvertently to take some action which installs ransomware on their system and spreads over the network by finding loopholes in the same as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Typical Phishing Operation
However, the modus operandi to drop ransomware in an organisation’s network has also changed nowadays, apart from the increase in ransom, thereby putting organisations in a tight spot.
Read More: Things You Should Know About Ransomware As A Service (RaaS)
Nowadays, phishing is used in multi-step ransomware operations rather than directly distributing ransomware. Figure 2, shows a typical multi-step ransomware operation.
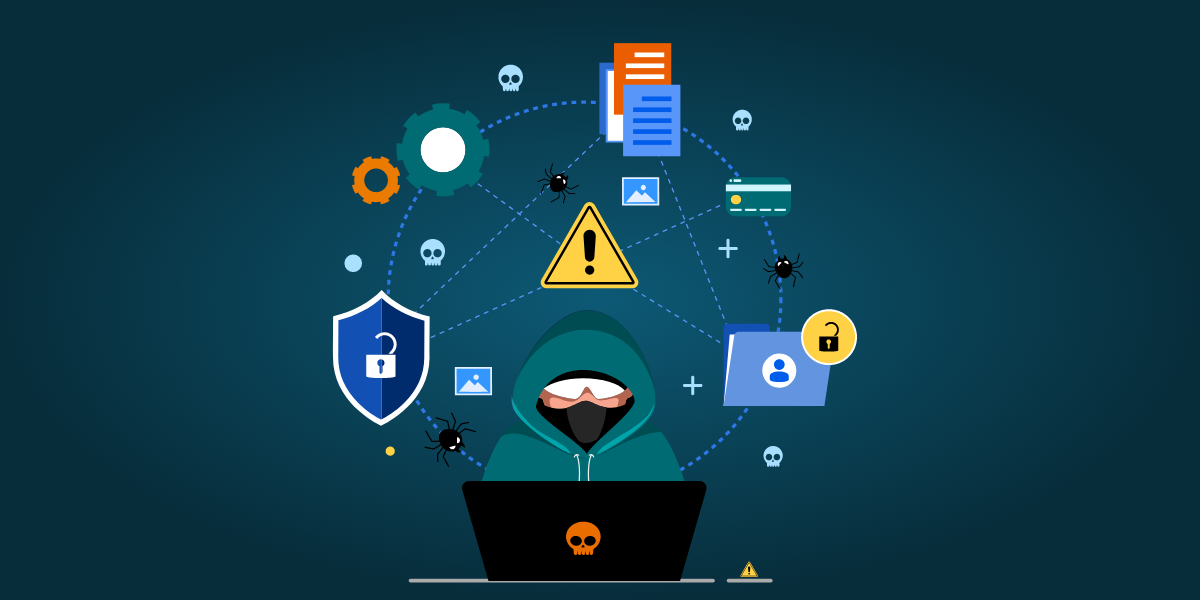

Figure 2: Multi-step ransomware operation
This tactic is used to divert initial security controls and collect information from the initially compromised system if threat actors deem it as a lucrative option. Through reconnaissance, the threat actors decide the initial target to gain entry into the organisation. This is also because ransomware operations are more profitable for the threat actors when they require manual effort from the organisation’s employees, who would end up compromising mostly the entire network. Once inside the compromised network, the malware can move laterally, stay put, increase its privileges and deliver the final payload. Because of all this, by the time the AntiVirus product can detect its binary, mitigating the impact may be too late. Therefore, it is always better if the AntiVirus vendors try to detect the ransomware at the phishing stage.
To mitigate the risk of an attack, it is crucial to educate users about old and contemporary phishing trends. Also, it is advisable to use a reputable security product such as “K7 Total Security” and keep it up to date to stay protected from such threats.